Our digestive tract contains about 2 kg of microbes (the microbiome). These microbes, often referred to as friendly bacteria, help with digestion, the production of vitamin B and vitamin K, and play a major role in the immune system.
A recent study published in Nature has found that statins disturb the gut microbiome - they inhibit the growth of some potentially useful bacteria in the gut and allow other bacteria to flourish and become superbugs resistant to antibiotics.
The study found that a wide range of commonly prescribed medications interfere with the gut microbiome, including simvastatin.
The study confirms what has previously been seen in studies done on mice given statins. These previous studies have found that rosuvastatin, atorvastatin and pravastatin also cause profound alterations in the balance of gut microbes. And this imbalance is similar to what has been seen in diet-related obesity.
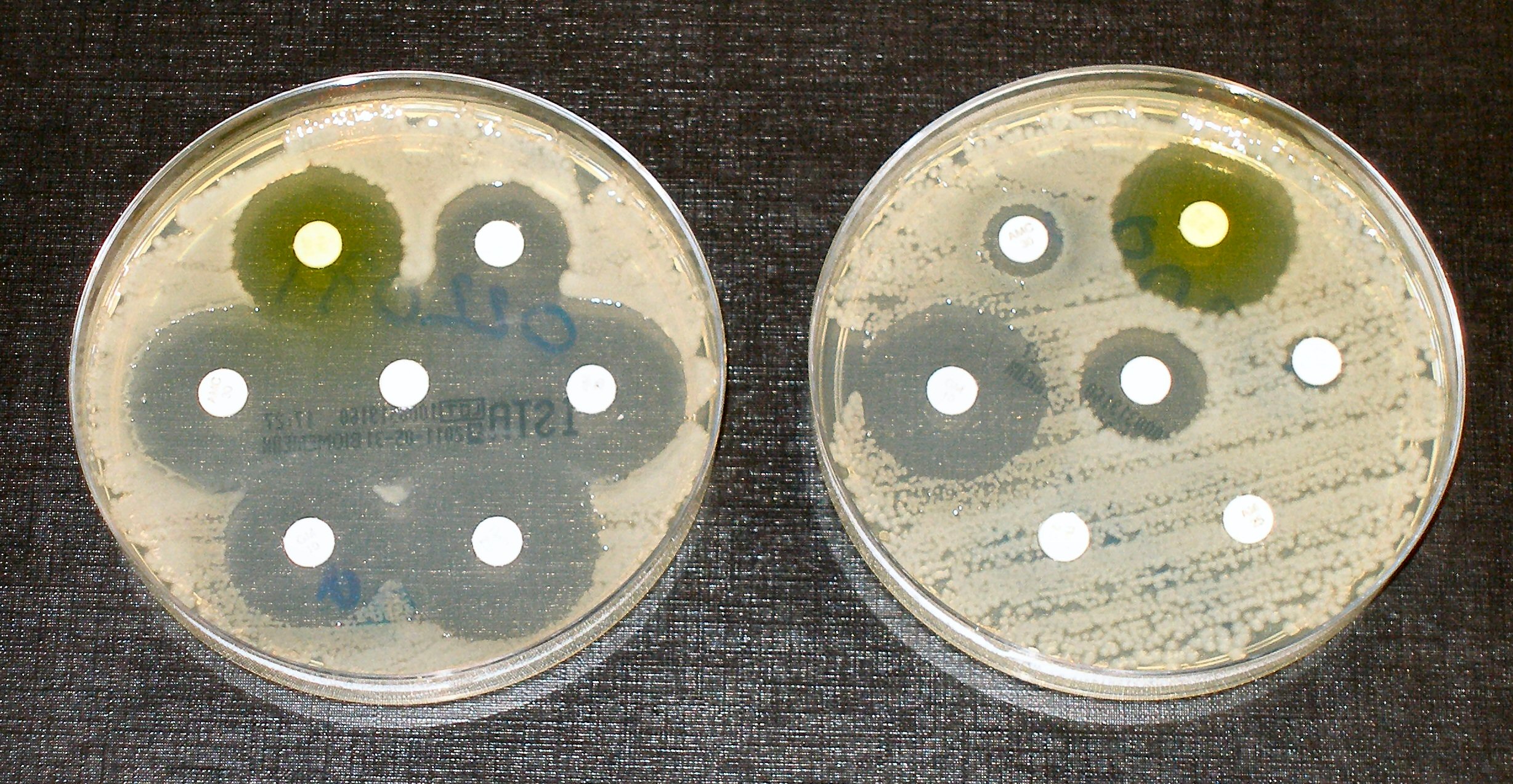
Antibiotic Resistance -the white paper discs contain antibiotics. Most of the bacteria in the dish on the left are sensitive to the antibiotics. The bacteria in the dish on the right are resistant to antibiotics.
The human body contains about one third more bacteria cells than human cells, and scientists are still investigating the many ways that these colonies of bacteria live in symbiosis with us. The implications of the changes in the bacteria caused by statins is difficult to predict, however the changes are likely to weaken the host's immune system and ability to produce some specific nutrients. Researchers for the article published in Nature say that statins are also contributing to the global problem of antibiotic resistance.
Antibiotic resistance, according to the World Health Organisation, is one of the most urgent public health problems and “Antibiotic resistance is rising to dangerously high levels in all parts of the world”.
This is an important example of how medicine has become unsustainable. This will likely become yet another serious adverse effect of the widespread use of statins that will simply be ignored in the push to keep hundreds of millions of healthy people as patients for profit.
References:
Maier, L et al. Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature doi:10.1038/nature25979. https://www.nature.com/articles/nature25979
Caparros-Martin, JA et al. Statin therapy causes gut dysbiosis in mice through a PXR-dependent mechanism. Microbione 2017; 5: 95. doi: 10.1186/s40168-017-0312-4. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5550934/
Nolan, JA et al. The influence of rosuvastatin on the gastrointestinal microbiota and host gene expression profiles. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017 May 1;312(5):G488-G497. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00149.2016. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28209601
Antibiotic Resistence – World Health Organisation. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/antibiotic-resistance/en/
Daily Mail. http://www.dailymail.co.uk/health/article-5521767/Statins-hayfever-pills-fueling-antibiotic-resistance.html
The Telegraph. https://www.telegraph.co.uk/science/2018/03/19/statins-hayfever-pills-could-driving-antibiotic-resistance-warn/
Image Source: Dr Graham Beards at en.wikipedia [CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0) or GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html)], via Wikimedia Commons